Japan (JA)
国・地域を選択してください。
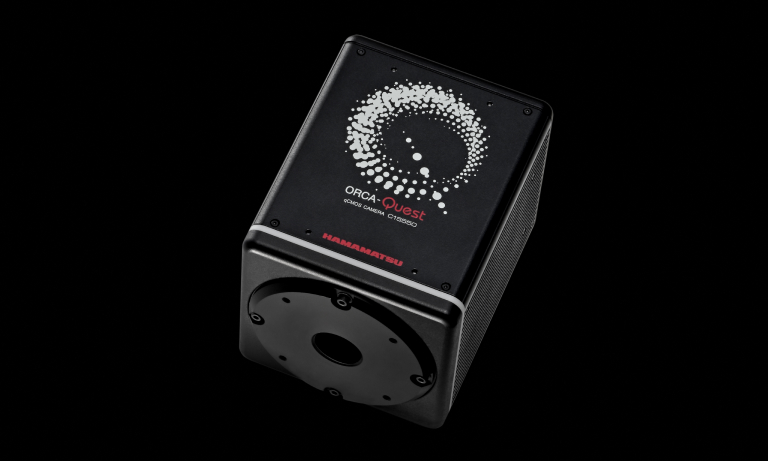
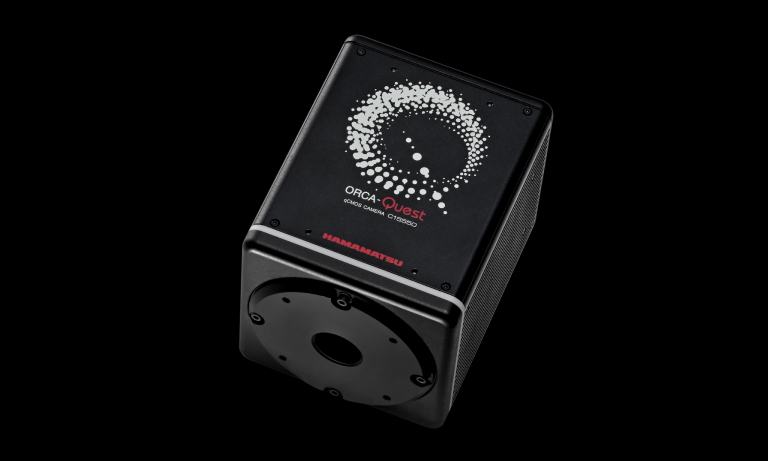
ORCA-Quest 2 qCMOSカメラ
C15550-22UP
Single photon countingから、Photon number resolvingへ
ORCA-Questは、独自の設計技術と最新の製造技術を駆使して開発したqCMOSイメージセンサを搭載し、世界で初めての光子数識別による究極の定量イメージングを実現しました。ORCA-Questの後継機として開発されたORCA-Quest 2は、極めて低ノイズなスキャンモードにおける読み出し速度の高速化や紫外領域での感度向上を実現しています。
ORCA、qCMOSは、浜松ホトニクス株式会社の登録商標です。
ORCA-Questに関するニュース記事
SPIE主催 Prism Awards 2022 Quantum部門ファイナリスト選出
ORCA-Quest からの進化
Ultra quiet scanの高速化
ORCA-Questはその極めて優れた低ノイズ性能から、光子数識別を実現するレベルにまで到達しました。
しかし、その性能を得るためにはカメラは比較的遅いスピードで撮像を行う必要があったため、使用可能なユーザーが限定されていました。ORCA-Quest 2ではセンサ駆動を最適化することで、従来と同等のノイズ性能を維持しながら、より高速なフレームレートを実現しています。この性能向上により、ほとんどのユーザーがORCA-Questの極めて優れた低ノイズ性能を活用できるようになりました。
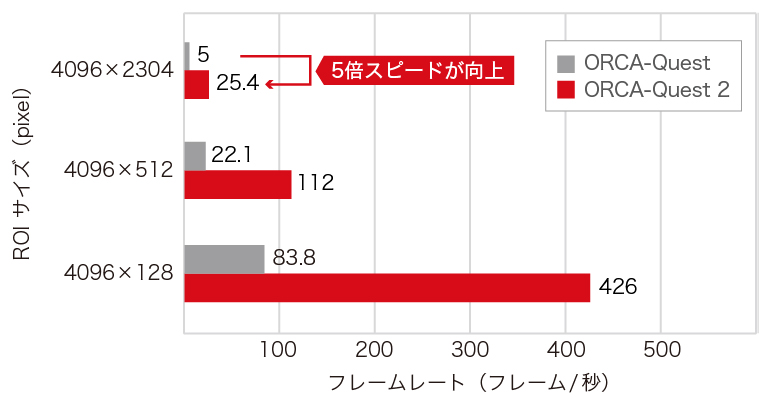
紫外感度向上
ORCA-Questは従来の科学計測用カメラと比べると、280 nm~400 nmの紫外波長領域で高い量子効率(QE)をもっていました。
ORCA-Quest 2では、市場のさらなる要望に応える形として、センサ窓のARコーティングを最適化することで、可視、近赤外波長領域のQEを減衰させることなく、さらに高い紫外領域のQEを実現しました。
この紫外感度向上により、イオントラップなどの量子技術といった、多くのアプリケーションでORCA-Questシリーズの汎用性を広げることができます。
Rawデータ出力
デジタル信号から光電子数を推定する、任意のアルゴリズムをユーザーが使用できるように、Rawデータの出力モードを搭載しました。
エッジトリガモードの高速化
新しいエッジトリガモードでは、ローリングシャッタ読み出し中に外部トリガを入力して露光を開始できるようになったため、フレームレートがより高速になりました。
4つの特長
微弱光を高S/N で検出するために、ORCA-Quest 2では、センサの構造からエレクトロニクスまでのありとあらゆる部分の最適化を図った設計を行いました。さらに最新のCMOS テクノロジーを使用したカスタムセンサを開発することにより、0.30 electrons rms という極めて優れた低ノイズ性能を実現することができました。


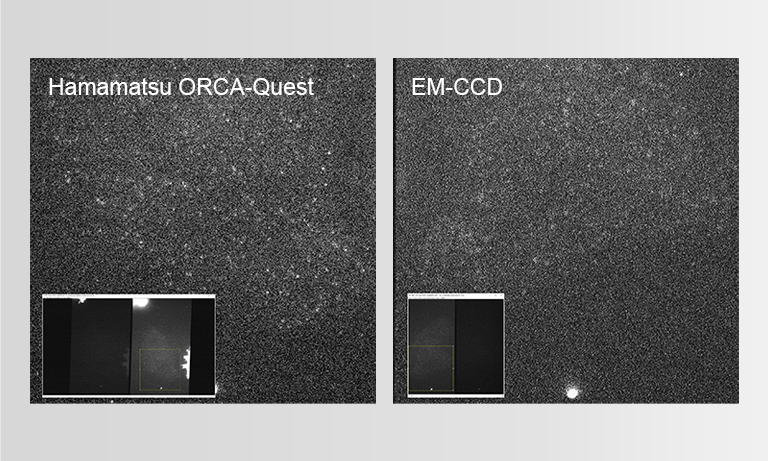
ピクセルあたり平均1フォトン入射画像(疑似カラー表示)の比較
露光時間:200 ms 表示レンジ:最小 ~ 最大カウント値 比較範囲:512 pixels × 512 pixels
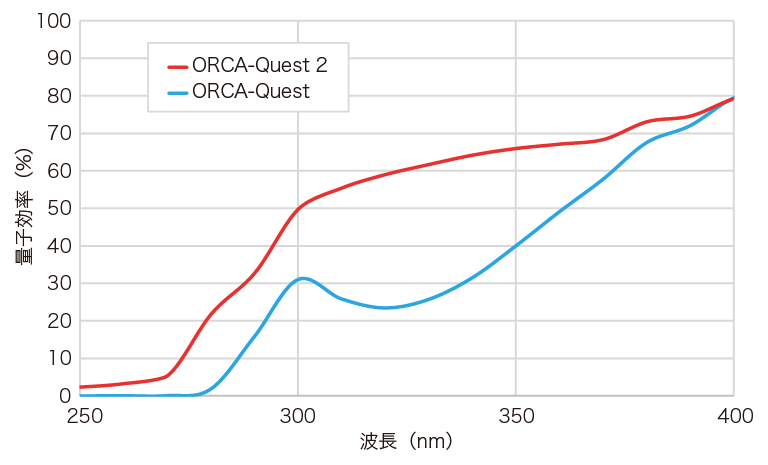
「光」とは、多数の「光子(Photon)」の集まりです。光子はセンサ上で電子に変換され、この電子を「光電子(Photoelectron)」といいます。光電子を数えることにより、光を正確に計測する方法が「光子数識別(Photon number resolving)※」です。
光電子を数えるためには光電子の信号量よりカメラ側のノイズが十分に小さい必要があります。従来のsCMOSカメラも読み出しノイズを小さく抑えていますが、それでも光電子の信号量よりもノイズは大きく、光電子を数えることは困難でした。
ORCA-Quest 2では、0.30 electrons rms(@Ultra quiet scan)という低読み出しノイズおよび、温度や時間に対する安定性、各画素値の個別校正とリアルタイム補正などの高度なカメラ技術の投入により、光子数識別を実現しています。
※光子数識別とは「光電子」の数を識別するもので、正確には「光子の検出」とは異なります。しかし、この分野における類似の手法である単一の光電子検出に対して「単一光子検出(Single photon counting)」という用語が用いられていることから、「光子数識別(Photon number resolving)」という用語を使用しています。
光電子の確率分布シミュレーションデータ (1画素あたりの平均発生光電子数 2 electrons)
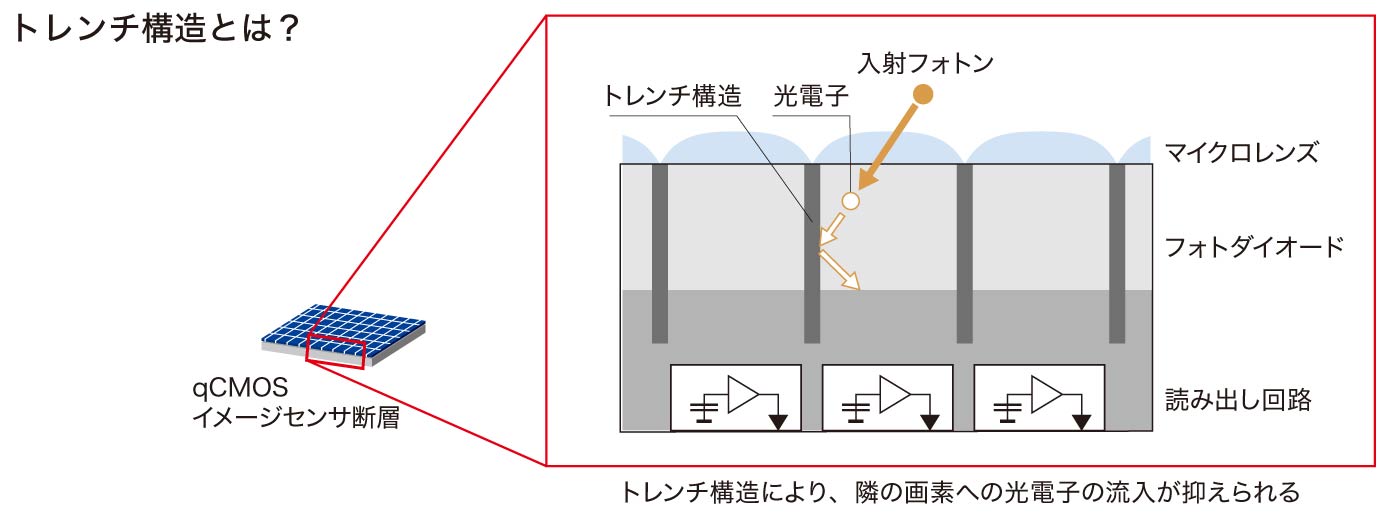
効率よく光子を検出するためには高量子効率を実現することが不可欠であり、この一つの手段として、背面照射構造の採用があります。従来の背面照射型センサでは、画素の区切りがないため、画素間でクロストークが発生し、分解能は前面照射型センサに比べて通常劣ります。
ORCA-Quest 2では、背面照射構造によって高量子効率を実現するだけでなく、画素を一つ一つに区切るトレンチ構造を採用し、画素間クロストーク低減を実現しました。
MTF測定結果
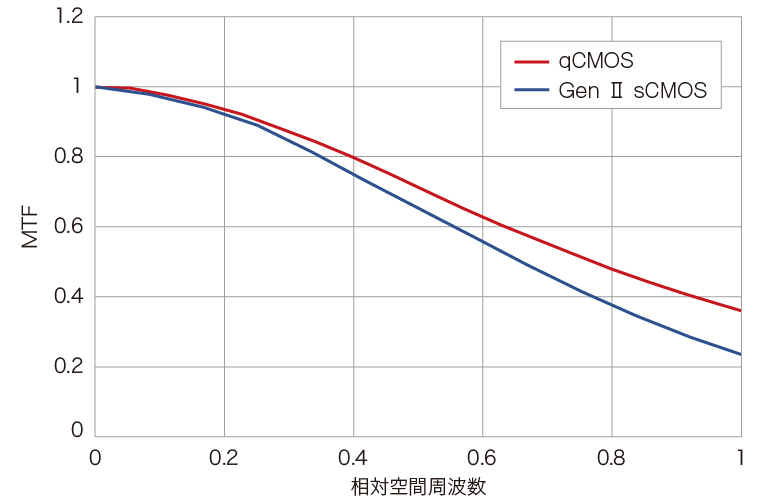
※MTFとは、Modulation Transfer Function の略で、分解能評価指標の一種です。被写体のコントラストをどれだけ正確に再現することができるかを示す値です。
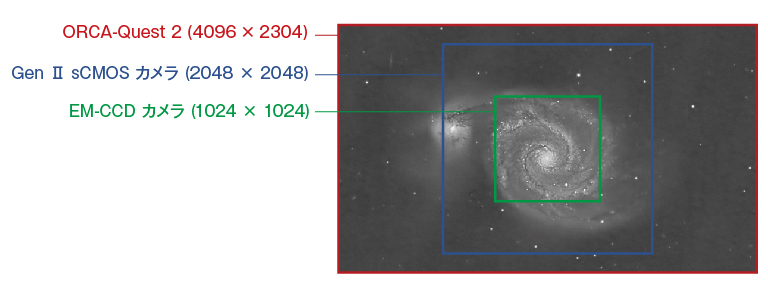
ORCA-Quest 2では、極低ノイズを実現しながらも、9.4メガピクセルの画素数(4096(H)× 2304(V))という高画素を実現することで、従来のGenⅡ sCMOSカメラ、EM-CCDカメラの画素数に比べて、一度により多くの対象物を撮像することが可能になりました。
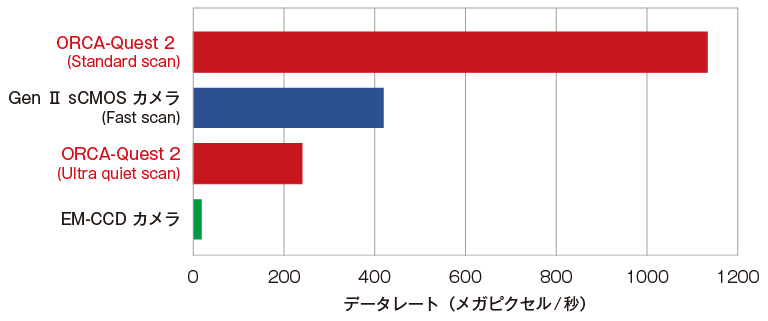
また、読み出し速度においてもORCA-Quest 2は突出した性能を持っています。ここでは、各カメラで画素数が異なるため、1秒間に読み出せる画素数であるデータレート(画素数 × フレームレート)で読み出し速度の比較をします。ORCA-Quest 2のStandard scanでは、0.43 electronsと従来のsCMOSカメラより読み出しノイズがさらに小さく、かつさらに高速なデータレートを実現しています。また、Ultra quiet scanでは、従来の単一光子検出カメラであるEM-CCDに対して、約10倍のデータレートで光子数識別イメージングが可能になります。
画素数比較
データレート比較
White paper
CMOS技術の絶え間ない進歩により、トランジスタの小型化、暗電流効果の低減、電子機器の読み出しノイズの低減が次々と実現されてきました。そして、イメージングの新たな時代の幕開けとなる新しい定量的CMOS(quantitative CMOS)技術が誕生。ピクセル内の光子数を確実に定量化するという物理的な限界についに到達し、技術による「解像度」「感度」「速度」のトレードオフを解消します。
qCMOS技術、Photon number resolving(光子数識別)の詳細は、以下のホワイトペーパーにてご紹介していますので、ぜひご覧ください。
※資料は英語版のみです。
カメラトピックス
qCMOSカメラ vs EM-CCDカメラ vol.1 – フォトンカウンティングカメラの性能比較
qCMOSカメラ vs EM-CCDカメラ vol.2 – 量子ビット状態検出
用途
中性原子、イオントラップ
量子コンピューティングにおける量子ビット(Qubit)として、中性原子やイオンは、一つ一つ、真空中にトラップ、配列されて計算に使用されます。それらの量子状態は蛍光を発するかどうかで判定することができますが、その蛍光計測は短時間かつ低光量下で行われるため、高速かつ低ノイズな光検出器が必要となります。
ORCA-Quest 2はその低ノイズ、高速な読み出し速度から、原子アレイの全体像観測だけでなく、個々の量子ビットの状態判定を行うことが可能です。

Rb原子アレイの蛍光イメージング (カメラ:ORCA-Quest)
提供:大阪大学 山本俊 様、小林俊輝 様
量子光学
量子光学の研究では、光子の量子的性質を研究、利用するために単一光子源を使用します。その際に、同様に単一光子検出器が必要となり、近年では検出器に入射した光子の数を識別できる検出器の必要性が出てきています。
カメラ技術の新たなコンセプトである、光子数識別可能なカメラが、この分野で新たな発見をもたらすことが期待されています。
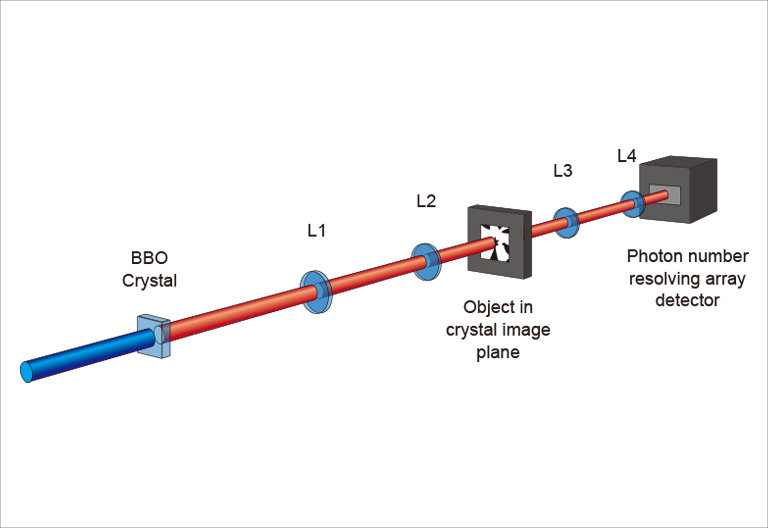
量子イメージングの実験構成

量子イメージング画像 (カメラ:ORCA-Quest)
提供:Prof. Miles Padgett 様 (University of Glasgow)
お客様導入事例
超解像顕微鏡法
超解像顕微鏡法とは回折限界を越える空間分解能を得るための手法を指しており、高い空間分解能を得るために低ノイズ、かつ小ピクセルサイズの科学計測用カメラを必要とします。
超解像画像 ORCA-Quest

qCMOSカメラ / 4.6 μm pixel size / 超解像システム:VT-iSIM
超解像画像 ORCA-Fusion

Gen Ⅲ sCMOSカメラ / 6.5 μm pixel size / 超解像システム:VT-iSIM
実験セットアップ(カメラ:ORCA-Quest)

提供:Steven Coleman 様 (VisiTech international Ltd.)
生物発光計測
近年、生物発光顕微鏡法が、従来の蛍光顕微鏡法に対して、励起光を必要としないなどユニークな特徴をもつという理由から注目を集めています。生物発光の主な欠点としては、その非常に小さい発光量が挙げられており、十分な画質の画像を取得することが難しいことにあります。そのため、生物発光の観測には長い露光時間を必要とするため、長時間露光下でも十分に高感度なカメラが必要とされます。
2波長同時発光イメージング
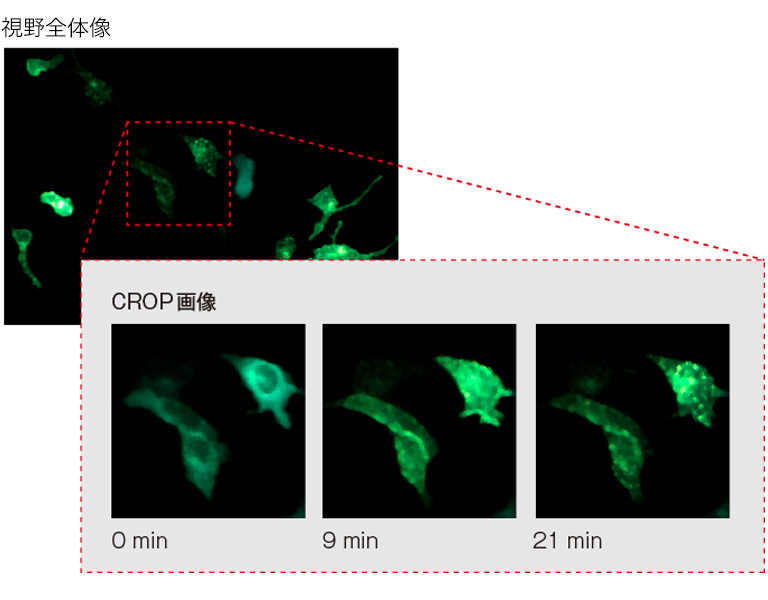
NanoLuc融合たんぱく質ARRB2と、Venus融合たんぱく質V2Rが近接してBRETが起きている様子
カメラ:ORCA-Quest + W-VIEW GEMINI
対物レンズ:20×、露光時間:30 s、ビニング:4×4
顕微鏡システム外観
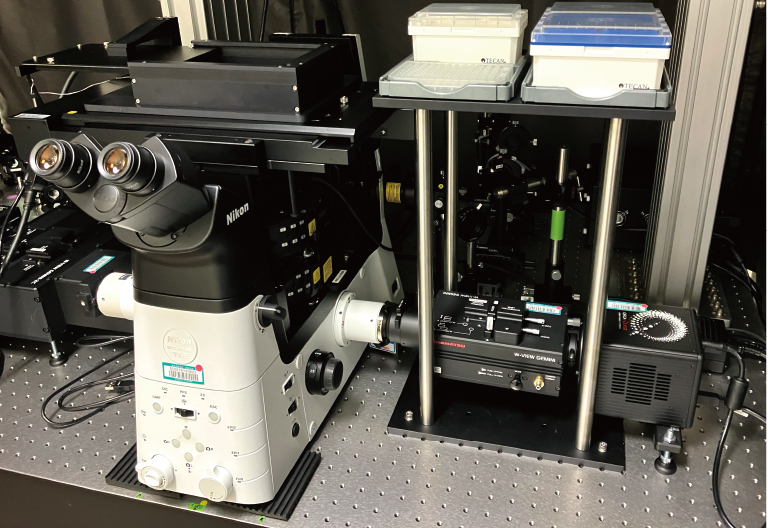

提供:東北大学大学院薬学研究科 分子細胞生化学分野 柳川正隆 様
植物の遅延蛍光
植物は光合成のために吸収した光エネルギーのごく一部を、時間をかけて光として放出します。この現象は遅延蛍光と呼ばれています。この僅かな光を検出することにより、化学物質、病原体、環境、その他ストレス要因が植物に与える影響を観察することが可能です。
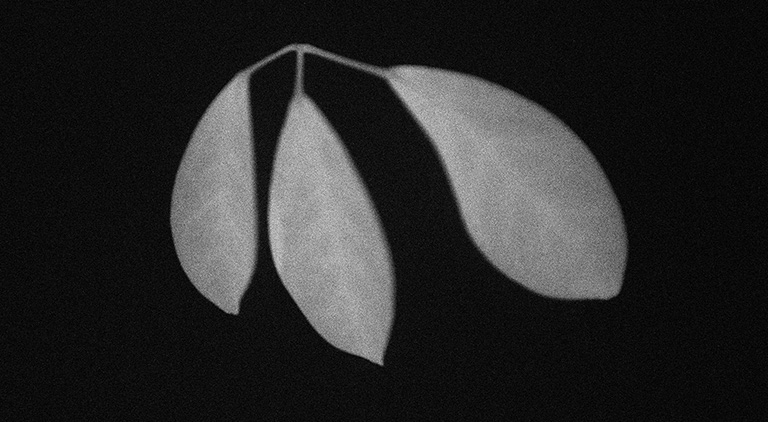

遅延蛍光(励起光消光後、10 秒経過してから10秒間露光)
お客様導入事例
ラッキーイメージング
地上から星を観察する場合、大気のゆらぎにより、星像がぼけます。しかし、短時間露光であれば、その時間内では大気が安定し、きれいな画像が得られることがあります。このため多くの画像を取得し、きれいな画像のみを位置を合わせながら積算する手法がラッキーイメージングです。

オリオン座大星雲 3波長フィルタを使用したカラー画像

顕微鏡システム外観
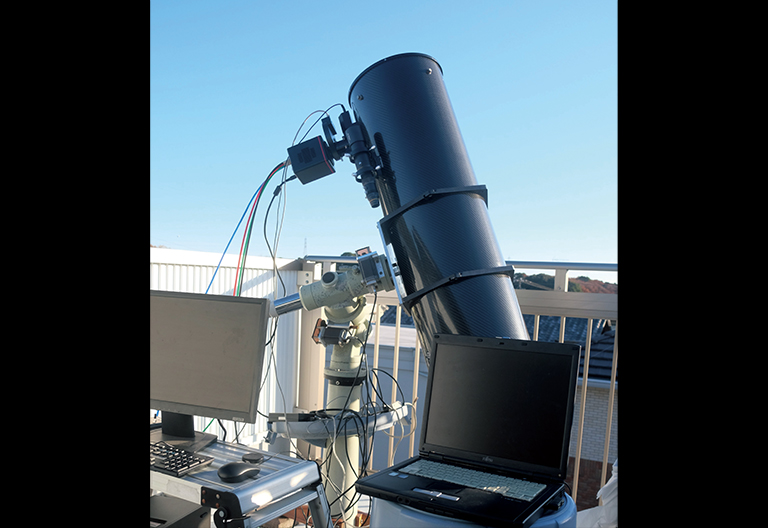
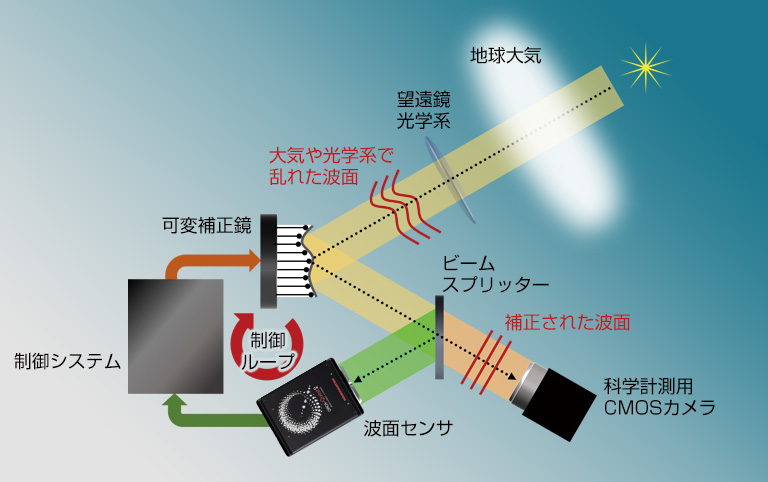
補償光学
補償光学技術は、大気ゆらぎにより乱れた波面を即時に補正し、望遠鏡の性能限界における最も歪みのない鮮明な星像を得る手法です。リアルタイムかつ高精度な波面補正を実現する装置にするため、波面の乱れを測定するカメラには、高速な読み出し性能と高い分解能が求められます。また、より暗い天体やレーザ人工星など、非常に光子数が少ない状況で波面補正が行われる場合もあり、カメラには高い感度が必要となります。
補償光学で波面を補正
補償光学 比較
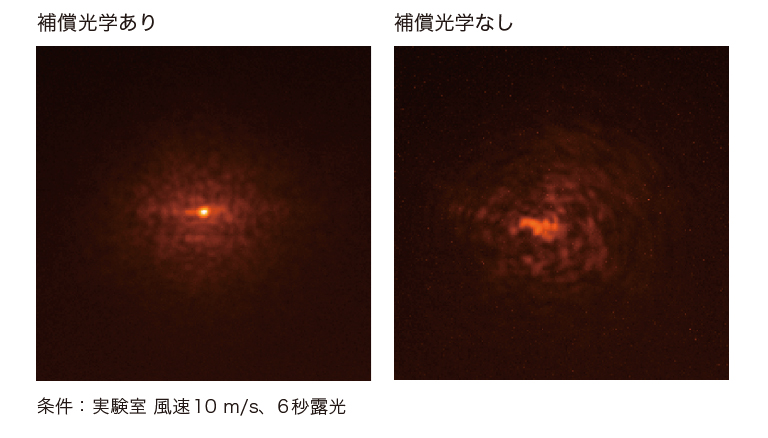
提供:京都大学大学院理学研究科附属天文台 山本広大 様
お客様導入事例
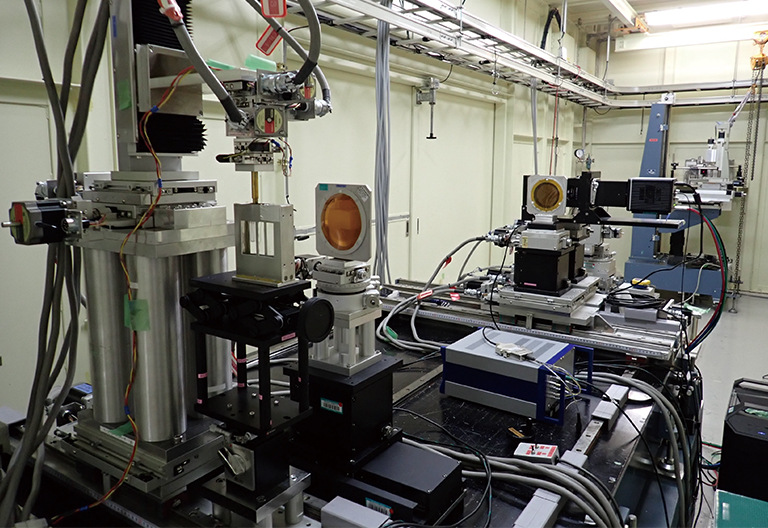
X線や高エネルギー粒子のイメージング用途で、可視光に変換するシンチレータをカップリングした科学計測用カメラが使用されています。瞬間的な現象をリアルタイム検出するために、低ノイズかつ高速なイメージング検出システムを必要としています。
マウス胎仔のX線位相CT像
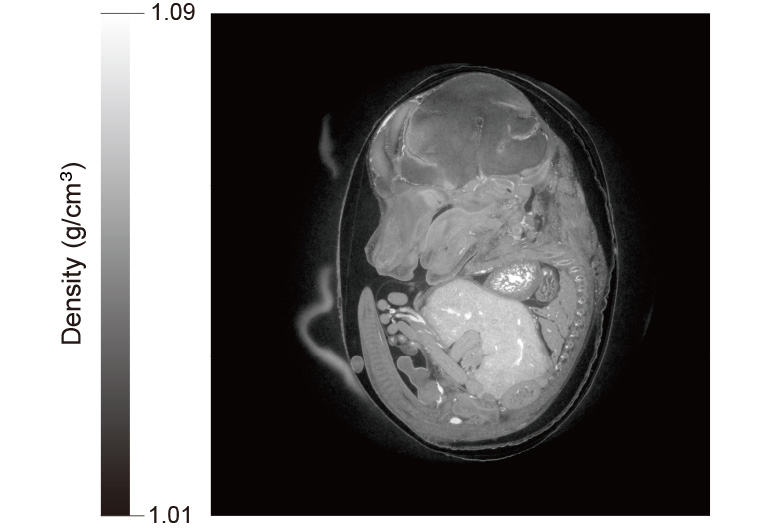
カメラ:ORCA-Quest / 光学系:高解像度X線イメージングユニット(M11427) / ビームライン:SPring-8 BL20B2 / 露光時間:15 ms / トータル計測時間:6.5 min
測定光学系全景

カメラ付近拡大
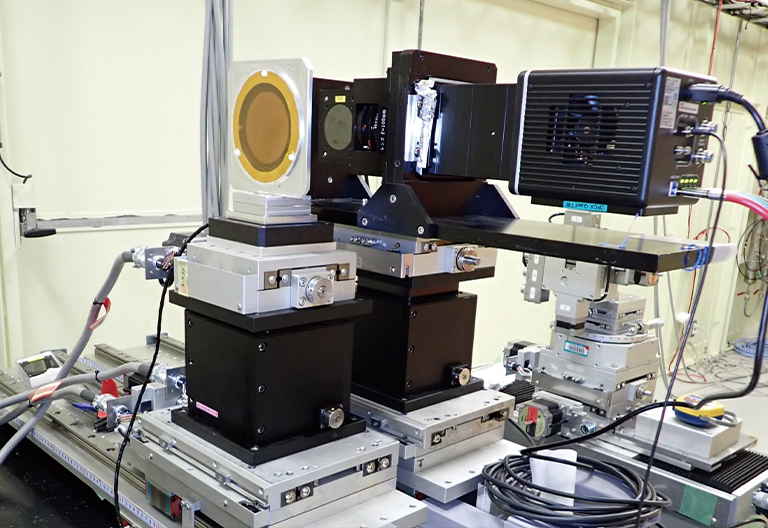

提供:高輝度光科学研究センター 放射光利用研究基盤センター 散乱・イメージング推進室 顕微・動的画像計測チーム 星野真人 様
お客様導入事例
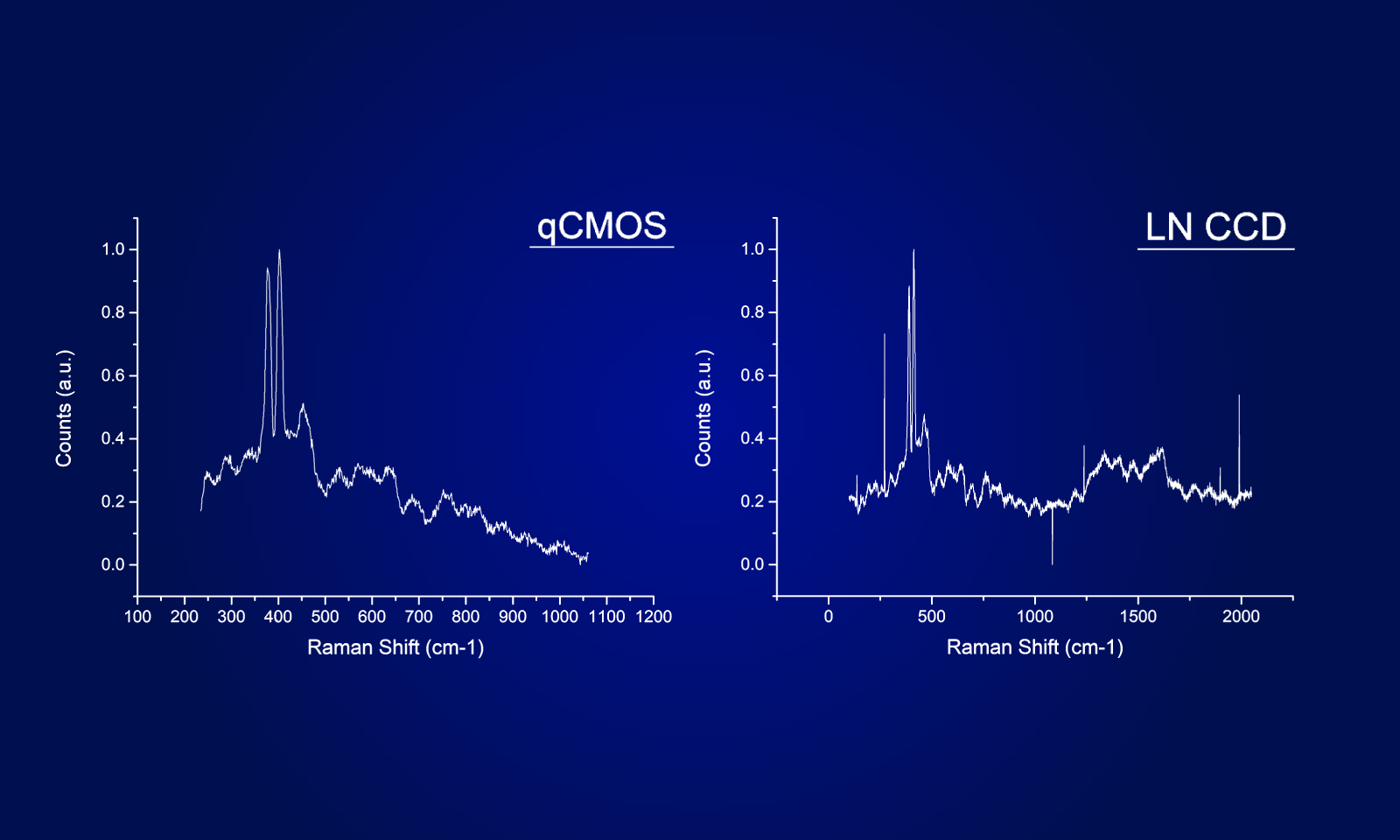
物質に光を照射すると、光と物質の相互作用が発生します。このうち、入射光とは異なる波長に散乱されるものをラマン散乱と呼び、この波長を測定することにより、物質の特性を測定する手法をラマン分光と言います。ラマン分光により、分子レベルの構造解析が可能であり、これにより化学結合、結晶性等の情報が得られます。
ラインスキャン型ラマンイメージングシステムにおけるORCA-QuestとEMCCDのスペクトル比較(1画素の光量が等しい条件)
ラマン画像

ORCA-Quest

EM-CCDカメラ
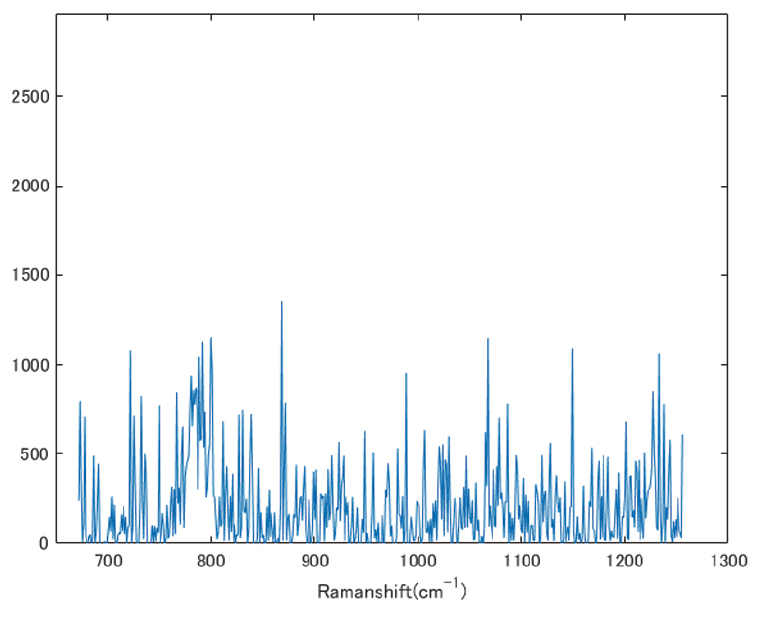
@10 photon/pixel/frame, 532 nm laser excitation
参考文献
ORCA-Quest
| アプリケーション | タイトル | 著者 | 書名 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quantum Computing | A fault-tolerant neutral-atom architecture for universal quantum computation | Dolev Bluvstein, Alexandra A. Geim, Sophie H. Li, Simon J. Evered, J. Pablo Bonilla Ataides, Gefen Baranes, Andi Gu, Tom Manovitz, Muqing Xu, Marcin Kalinowski, Shayan Majidy, Christian Kokail, Nishad Maskara, Elias C. Trapp, Luke M. Stewart, Simon Hollerith, Hengyun Zhou, Michael J. Gullans, Susanne F. Yelin, Markus Greiner, Vladan Vuletić, Madelyn Cain & Mikhail D. Lukin | Nature (2025) |
| Quantum Computing | A tweezer array with 6100 highly coherent atomic qubits | Hannah J. Manetsch, Gyohei Nomura, Elie Bataille, Kon H. Leung, Xudong Lv, Manuel Endres | Nature (2025) |
| Quantum Computing | Continuous operation of a coherent 3,000-qubit system | Neng-Chun Chiu, Elias C. Trapp, Jinen Guo, Mohamed H. Abobeih, Luke M. Stewart, Simon Hollerith, Pavel L. Stroganov, Marcin Kalinowski, Alexandra A. Geim, Simon J. Evered, Sophie H. Li, Xingjian Lyu, Lisa M. Peters, Dolev Bluvstein, Tout T. Wang, Markus Greiner, Vladan Vuletić & Mikhail D. Lukin | Nature (2025) |
| Quantum Computing | Logical quantum processor based on reconfigurable atom arrays | Dolev Bluvstein, Simon J. Evered, Alexandra A. Geim, Sophie H. Li, Hengyun Zhou, Tom Manovitz, Sepehr Ebadi, Madelyn Cain, Marcin Kalinowski, Dominik Hangleiter, J. Pablo Bonilla Ataides, Nishad Maskara, Iris Cong, Xun Gao, Pedro Sales Rodriguez, Thomas Karolyshyn, Giulia Semeghini, Michael J. Gullans, Markus Greiner, Vladan Vuletić & Mikhail D. Lukin | Nature (2023) |
| Quantum Imaging | Quantum imaging with a photon counting camera | Osian Wolley, Thomas Gregory, Sebastian Beer, Takafumi Higuchi , Miles Padgett | Scientific Reports volume 12, Article number: 8286 (2022) |
| Quantum Imaging | Observation of Nonclassical Photon Statistics in Single-Bubble Sonoluminescence | Mohammadreza Rezaee, etal. | arXiv:2203.11337 |
| Life Science | Unique algorithm for the evaluation of embryo photon emission and viability | József Berke, István Gulyás, Zoltán Bognár, Dávid Berke, Attila Enyedi, Veronika Kozma-Bognár, Péter Mauchart, Bernadett Nagy, Ákos Várnagy, Kálmán Kovács & József Bódis | Nature (2024) |
| Life Science | Volumetric imaging of fast cellular dynamics with deep learning enhanced bioluminescence microscopy | Luis Felipe Morales-Curiel, et al. | Commun Biol 5, 1330 (2022). |
| Life Science |
Multiphoton imaging using a quantitative CMOS camera | Mbaye Diouf, et al. | Proceedings Volume 11965, Multiphoton Microscopy in the Biomedical Sciences XXII; 119650D (2022) |
| Astronomy | qCMOS Detectors and the Case of Hypothetical Primordial Black Holes in the Solar System, near Earth Objects, Transients, and Other High-cadence Observations | Martin M. Roth | Res. Notes AAS 8 282 (2024) |
| Astronomy | Photonic spectro-interferometry with SCExAO/FIRST at the Subaru Telescope: towards H-alpha imaging of protoplanets | Sébastien Vievard, et al. | Proc. SPIE 12680, Techniques and Instrumentation for Detection of Exoplanets XI, 126800H (5 October 2023) |
| HEP/Synchrotron | X-ray imaging with Micromegas detectors with optical readout | A. Cools, et al | JINST 18 C06019 |
| HEP/Synchrotron | Sub-micrometer real-time imaging of trajectory of alpha particles using GAGG plate and CMOS camera | Seiichi Yamamoto, et al. | 2024 JINST 19 P01010 |
| HEP/Synchrotron | Rational partitioning of spectral feature space for effective clustering of massive spectral image data | Yusei Ito, Yasuo Takeichi, Hideitsu Hino, Kanta Ono | Scientific Reports volume 14, Article number: 22549 (2024) |
| Image Sensors | Efficient and accurate conversion-gain estimation of a photon-counting image sensor based on the maximum likelihood estimation | Katsuhiro Nakamoto and Hisaya Hotaka | Opt. Express 30, 37493-37506 (2022) |
ソフトウェア
仕様
| 型名 | C15550-22UP |
|---|---|
| 撮像素子 | qCMOSイメージセンサ |
| 有効画素数 | 4096(H)× 2304(V) |
| 画素サイズ | 4.6 μm(H)× 4.6 μm(V) |
| 有効素子サイズ | 18.841 mm(H)× 10.598 mm(V) |
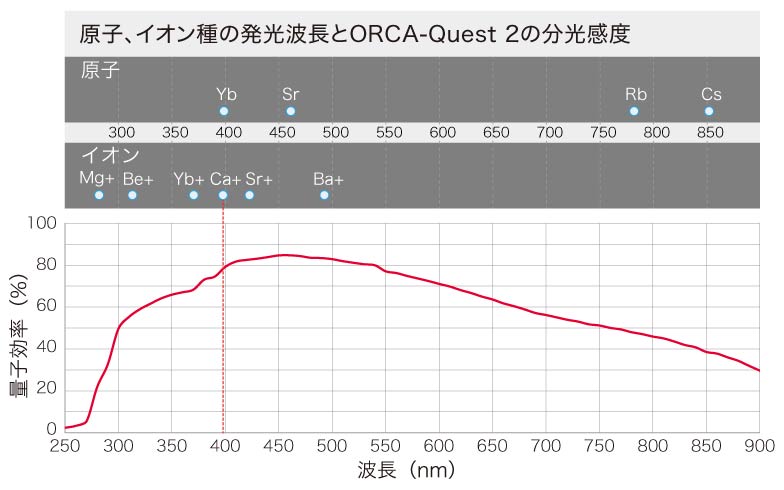
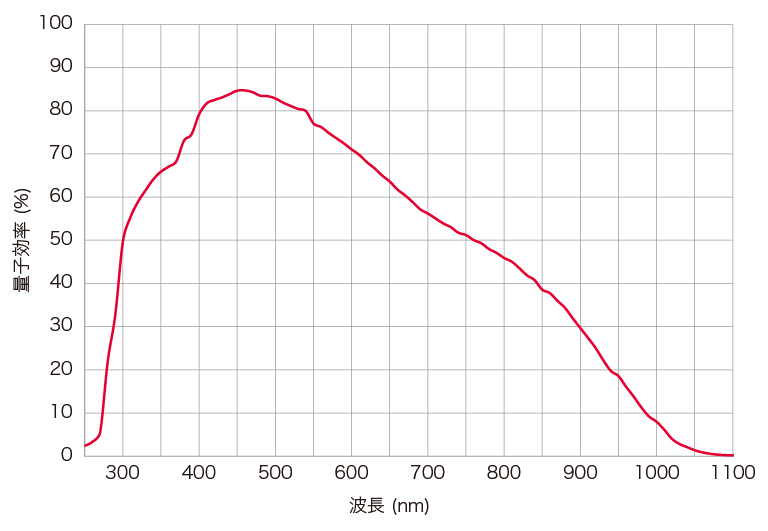
| 量子効率(typ.) | 85 %(ピーク時) |
| 飽和電荷量(typ.) | 7000 electrons |
| 読み出しノイズ(typ.) | Standard scan:0.43 electrons(rms)、 0.39 electrons(median) Ultra quiet scan:0.30 electrons(rms)、0.25 electrons(median) |
| ダイナミックレンジ(typ.)*1 | 23 000 : 1 (rms)、28 000 : 1 (median) |
| 暗出力不均一性 (DSNU) (typ.) *2 | 0.06 electrons |
| 感度不均一性 (PRNU) (typ.) *2*3 | 0.1 % 未満 |
| リニアリティエラー | 0.5 % |
| 冷却方式(ペルチェ冷却) | 強制空冷(周囲温度+25 ℃):-20 ℃ 水冷(水温+25 ℃)*4:-20 ℃ 水冷[最大冷却(水温+20 ℃、周囲温度+20 ℃ 時)]*4:-35 ℃(typ.) |
| 暗電流(typ.) | 強制空冷(周囲温度+25 ℃):0.016 electrons/pixels/s 水冷(水温+25 ℃)*4:0.016 electrons/pixels/s 水冷[最大冷却(水温+20 ℃、周囲温度+20 ℃ 時)]*4:0.006 electrons/pixels/s |
| 読み出し速度 | Standard scan *5:全画素読み出し時、120フレーム/秒(CoaXPress動作)、17.6フレーム/秒(USB動作) Ultra quiet scan、PNR、Raw:全画素読み出し時、25.4フレーム/秒(CoaXPress動作)、17.6フレーム/秒(USB動作) |
| 露光時間 | Standard scan *5:7.2 μs~1800 s Ultra quiet scan、PNR、Raw:33.9 μs ~ 1800 s *6 |
| 外部トリガモード | エッジトリガ、グローバルリセットエッジトリガ、レベルトリガ、グローバルリセットレベルトリガ、読み出し同期トリガ、スタートトリガ |
| トリガ遅延機能 | 0 μs ~ 10 s(1 μs ステップ) |
| トリガ出力 | グローバル露光タイミング出力、エニーロー露光タイミング出力、トリガレディ出力、プログラマブルタイミング出力×3系統、ハイ出力、ロー出力 |
| デジタル出力 | 16 bit、12 bit、8 bit |
| 画像処理機能 | 欠陥画素補正(ON-OFF 可能、白点補正3段階選択可) |
| エミュレーションモード | 有(ORCA-Quest、ORCA-Fusion) |
| インターフェース | USB 3.1 Gen 1、CoaXPress (Quad CXP-6 ) |
| 入力コネクタ | SMA |
| 出力コネクタ | SMA |
| レンズマウント | Cマウント*7 |
| 電源 | AC 100 V ~ AC 240 V、50 Hz/60 Hz |
| 消費電力 | 約155 VA |
| 動作周囲温度 | 0 ℃ ~ +40 ℃ |
| 動作周囲湿度 | 30 % ~ 80 %(結露しないこと) |
| 保存周囲温度 | -10 ℃ ~ +50 ℃ |
| 保存周囲湿度 | 90 %以下(結露しないこと) |
*1:飽和電荷量とUltra quiet scan時の読み出しノイズから算出
*2:Ultra quiet scan時の値
*3:3500 electrons、中心 1500 × 1500、1000枚積算時の値
*4:冷却水の水量は0.46 L/分
*5:エリア読み出しのみ
*6:グローバルリセットエッジトリガ及びグローバルリセットレベルトリガでは、露光時間の最小は67.8 μs
*7:Fマウント対応の製品(C15550-22UP01)もございます。ご希望の場合、当社までお問い合わせください。Fマウントは構造上光漏れがあり、特に長時間露光測定ではその影響を受ける可能性があります。
分光感度特性
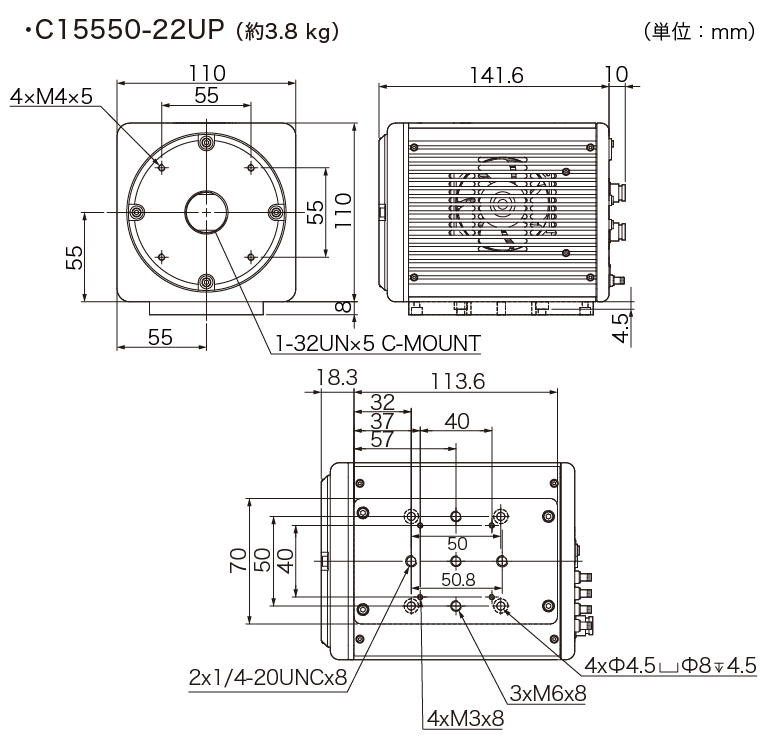
外形寸法図
関連資料
技術資料(旧モデル、ORCA-Quest用)
アプリケーションノート
シミュレーションラボ
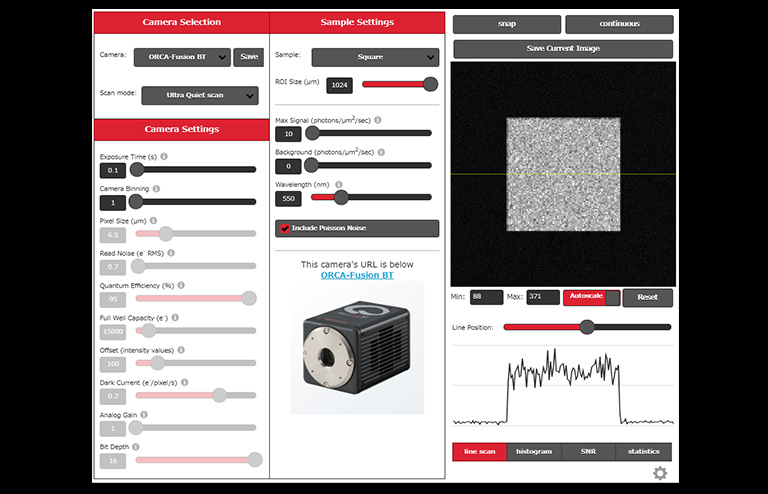
産業用・研究用途でカメラを用いる場合、撮影する対象の波長や光量など、様々な条件を考慮してカメラを選定する必要があります。
弊社では、シミュレーション画像を確認しながら直感的にカメラの性能によるイメージングの結果の違いなどを比較できるツール「カメラシミュレーションラボ」を提供しています。
カメラアプリケーション事例集
「放射光科学が解き明かす小惑星「リュウグウ」の物質構造 」カメラアプリケーション事例集
天文学者への貴重なインタビューやカメララインアップを掲載「Astronomy カメラアプリケーション事例集」
- Confirmation
-
It looks like you're in the . If this is not your location, please select the correct region or country below.
You're headed to Hamamatsu Photonics website for JP (Japanese). If you want to view an other country's site, the optimized information will be provided by selecting options below.
In order to use this website comfortably, we use cookies. For cookie details please see our cookie policy.
- Cookie Policy
-
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in this cookie policy. By closing the cookie warning banner, scrolling the page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to the use of cookies.
Hamamatsu uses cookies in order to enhance your experience on our website and ensure that our website functions.
You can visit this page at any time to learn more about cookies, get the most up to date information on how we use cookies and manage your cookie settings. We will not use cookies for any purpose other than the ones stated, but please note that we reserve the right to update our cookies.
1. What are cookies?
For modern websites to work according to visitor’s expectations, they need to collect certain basic information about visitors. To do this, a site will create small text files which are placed on visitor’s devices (computer or mobile) - these files are known as cookies when you access a website. Cookies are used in order to make websites function and work efficiently. Cookies are uniquely assigned to each visitor and can only be read by a web server in the domain that issued the cookie to the visitor. Cookies cannot be used to run programs or deliver viruses to a visitor’s device.
Cookies do various jobs which make the visitor’s experience of the internet much smoother and more interactive. For instance, cookies are used to remember the visitor’s preferences on sites they visit often, to remember language preference and to help navigate between pages more efficiently. Much, though not all, of the data collected is anonymous, though some of it is designed to detect browsing patterns and approximate geographical location to improve the visitor experience.
Certain type of cookies may require the data subject’s consent before storing them on the computer.
2. What are the different types of cookies?
This website uses two types of cookies:
- First party cookies. For our website, the first party cookies are controlled and maintained by Hamamatsu. No other parties have access to these cookies.
- Third party cookies. These cookies are implemented by organizations outside Hamamatsu. We do not have access to the data in these cookies, but we use these cookies to improve the overall website experience.
3. How do we use cookies?
This website uses cookies for following purposes:
- Certain cookies are necessary for our website to function. These are strictly necessary cookies and are required to enable website access, support navigation or provide relevant content. These cookies direct you to the correct region or country, and support security and ecommerce. Strictly necessary cookies also enforce your privacy preferences. Without these strictly necessary cookies, much of our website will not function.
- Analytics cookies are used to track website usage. This data enables us to improve our website usability, performance and website administration. In our analytics cookies, we do not store any personal identifying information.
- Functionality cookies. These are used to recognize you when you return to our website. This enables us to personalize our content for you, greet you by name and remember your preferences (for example, your choice of language or region).
- These cookies record your visit to our website, the pages you have visited and the links you have followed. We will use this information to make our website and the advertising displayed on it more relevant to your interests. We may also share this information with third parties for this purpose.
Cookies help us help you. Through the use of cookies, we learn what is important to our visitors and we develop and enhance website content and functionality to support your experience. Much of our website can be accessed if cookies are disabled, however certain website functions may not work. And, we believe your current and future visits will be enhanced if cookies are enabled.
4. Which cookies do we use?
There are two ways to manage cookie preferences.
- You can set your cookie preferences on your device or in your browser.
- You can set your cookie preferences at the website level.
If you don’t want to receive cookies, you can modify your browser so that it notifies you when cookies are sent to it or you can refuse cookies altogether. You can also delete cookies that have already been set.
If you wish to restrict or block web browser cookies which are set on your device then you can do this through your browser settings; the Help function within your browser should tell you how. Alternatively, you may wish to visit www.aboutcookies.org, which contains comprehensive information on how to do this on a wide variety of desktop browsers.
5. What are Internet tags and how do we use them with cookies?
Occasionally, we may use internet tags (also known as action tags, single-pixel GIFs, clear GIFs, invisible GIFs and 1-by-1 GIFs) at this site and may deploy these tags/cookies through a third-party advertising partner or a web analytical service partner which may be located and store the respective information (including your IP-address) in a foreign country. These tags/cookies are placed on both online advertisements that bring users to this site and on different pages of this site. We use this technology to measure the visitors' responses to our sites and the effectiveness of our advertising campaigns (including how many times a page is opened and which information is consulted) as well as to evaluate your use of this website. The third-party partner or the web analytical service partner may be able to collect data about visitors to our and other sites because of these internet tags/cookies, may compose reports regarding the website’s activity for us and may provide further services which are related to the use of the website and the internet. They may provide such information to other parties if there is a legal requirement that they do so, or if they hire the other parties to process information on their behalf.
If you would like more information about web tags and cookies associated with on-line advertising or to opt-out of third-party collection of this information, please visit the Network Advertising Initiative website http://www.networkadvertising.org.
6. Analytics and Advertisement Cookies
We use third-party cookies (such as Google Analytics) to track visitors on our website, to get reports about how visitors use the website and to inform, optimize and serve ads based on someone's past visits to our website.
You may opt-out of Google Analytics cookies by the websites provided by Google:
https://tools.google.com/dlpage/gaoptout?hl=en
As provided in this Privacy Policy (Article 5), you can learn more about opt-out cookies by the website provided by Network Advertising Initiative:
http://www.networkadvertising.org
We inform you that in such case you will not be able to wholly use all functions of our website.
Close