Japan (JA)
国・地域を選択してください。
生物発光顕微鏡の限界に挑む
生物の微弱な発光を用いて生きた細胞や動物を画像化する生物発光顕微鏡法は、蛍光顕微鏡法と比較して多くの利点があり、多くの研究者が生物発光顕微鏡の観察手法の開発を進めています。特に神経科学の研究において有効な手法であることが示されています。
Institut de Ciencies Fotòniques(ICFO)のMichael Krieg 様とその共同研究者は、生物発光顕微鏡の利点を明らかにし、また生物発光顕微鏡の限界を越えることで、線虫やその他のモデル生物で細胞動態を捉える高速な3次元イメージングを実現しました。
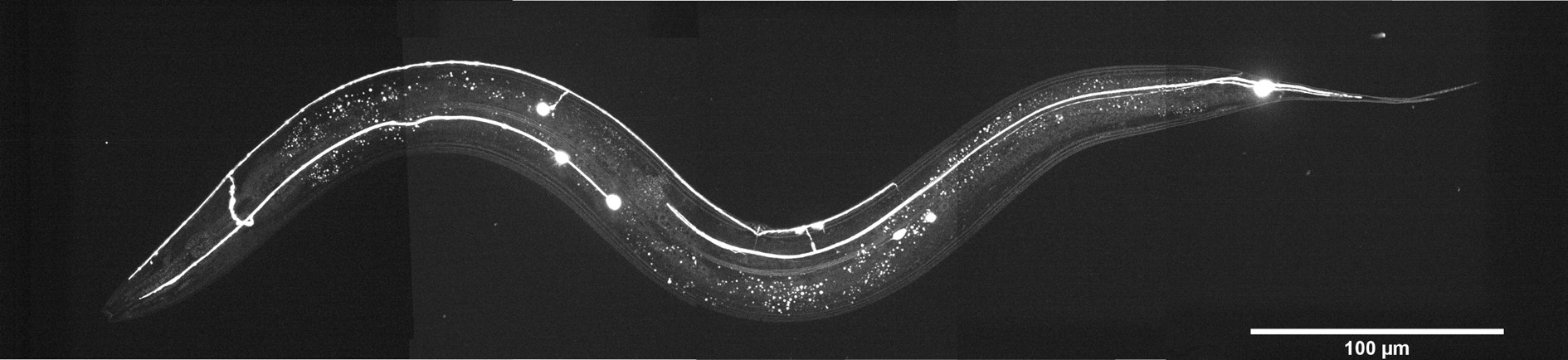
Caenorhabditis elegansは体長1 mmの小さな線虫で、過去60年間モデル生物として使用されてきました。 Copyright © 2022, Luis Felipe Morales-Curiel, Michael Krieg et al.
生物発光顕微鏡のメリットと課題
生物発光顕微鏡で観察するシグナルは、酵素(ルシフェラーゼ)と、その基質(ルシフェリン)の化学反応によって生成されます。生物発光顕微鏡の一般的なアプローチと得られる情報は蛍光顕微鏡と似ていますが、励起光を使用しない点が生物発光顕微鏡の大きな利点です。励起光を使用しないことで、サンプルの自家蛍光によるバックグラウンドシグナルが発生しないため、観察したい特定のシグナルが埋もれずに高いS/Nで観察ができます。
また、蛍光顕微鏡で使用されるような強い励起光は、応用例1に見られるようにサンプルに光毒性を引き起こす可能性があります。生物発光顕微鏡では励起光を当てないことでサンプルの光毒性を軽減できることも利点です。
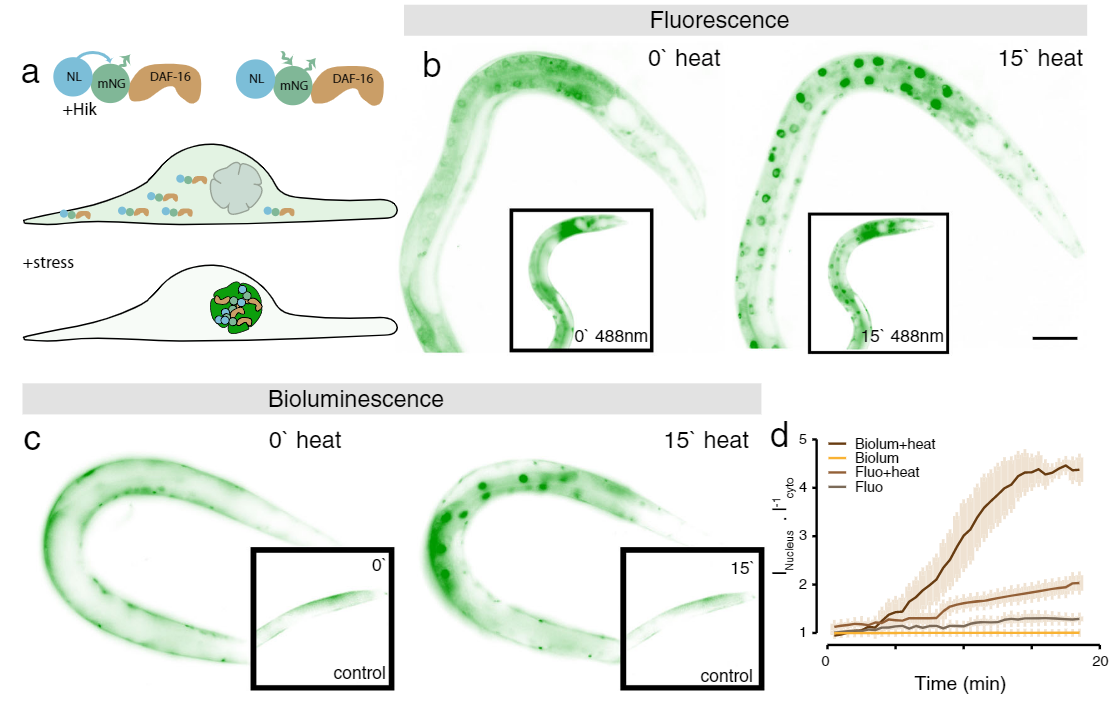
応用例1 : Fluorescence vs bioluminescence on C. elegans after induced stress1
ストレスレポーターとして働くDAF-16を融合したmNeonGreen-NanoLanternを用いて、線虫の細胞内ストレス応答を測定しました。ストレス要因がない場合、DAF-16は細胞質に存在しますが、ストレスがかかるとDAF-16のほとんどが核に存在するようになります。実験は、mNeonGreenの蛍光観察(図b)と、mNeonGreen-Nanolantern融合体を用いた発光観察(図c)で行いました。熱で刺激した後、ストレス応答は蛍光観察と生物発光観察の両方で検出されますが、生物発光のほうが特異的な自家蛍光が存在しないため、その変化は顕著に検出されます。興味深いことに、対照実験(図bおよび図c)では、おそらく励起光が原因で、蛍光観察にストレス応答が表れています。
また、蛍光マーカーは時間の経過とともに褪色しやすいため、生きたサンプルを長時間観察することは困難でした。生物発光顕微鏡では、信号の発生に必要なエネルギーを蛍光のような光物理学的プロセスではなく化学的プロセスから得るため、褪色の問題が起こりづらく、長時間の観察が可能になります。
しかし、生物発光は信号強度が非常に弱く、生物発光顕微鏡の観察は長時間の露光が必要となり、得られる画像が低S/Nな画像になります。そのため、生きたサンプルの観察において非常に重要である生物の動態観察が制限されてしまう点が欠点といえます。
実験系のセットアップについて
Michael Krieg 様のグループは、生物発光のための実験環境をあらゆる側面から最適化しました。生物発光イメージングの限界に挑戦するため、極端に光量を減らしたサンプルを使用し、高い時間分解能で高S/Nな画像を取得することを目指しました。その実現のために、古くから使用されているルシフェラーゼよりも明るく、スペクトル特性が多様なナノランタン(Nano Lantern)を使用しました。また、一般的な顕微鏡では十分な信号が得られないため、「LowLiteScope」と呼ばれる光の利用効率を高めた顕微鏡を製作しました。
さらに、実際に取得した画像はシグナルが非常に弱かったため、CARE (Content Awareness Image Restoration) を適用して画質を改善し、ミリ秒単位の露光時間で、鮮明でコントラストの高い画像を取得することができました。
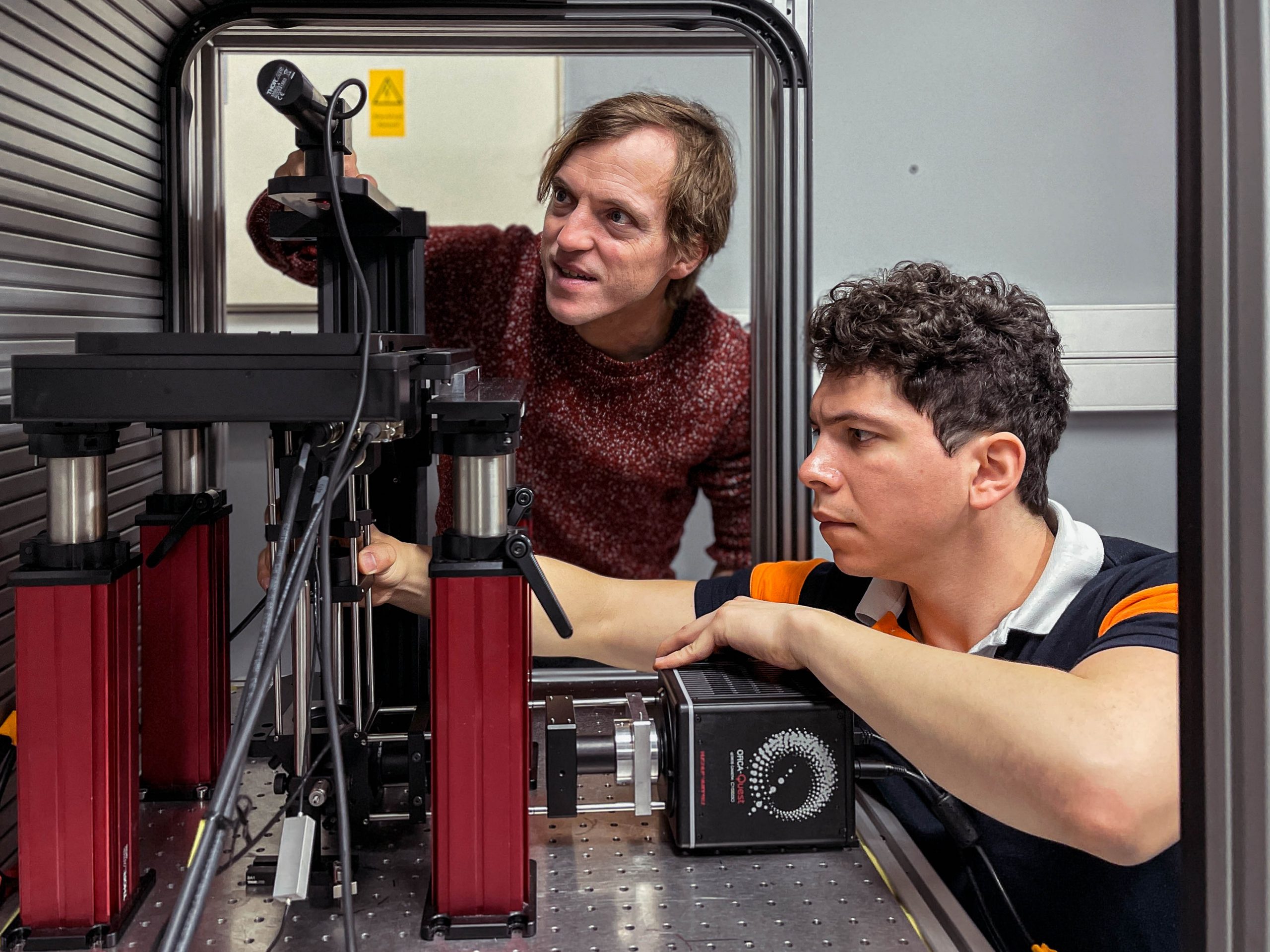

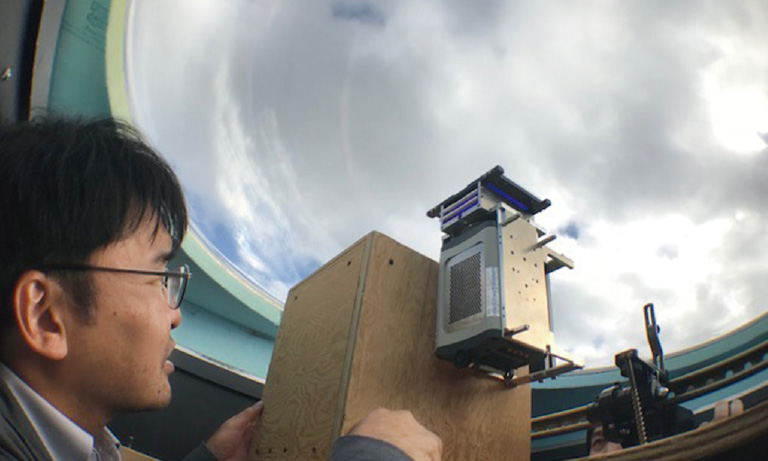
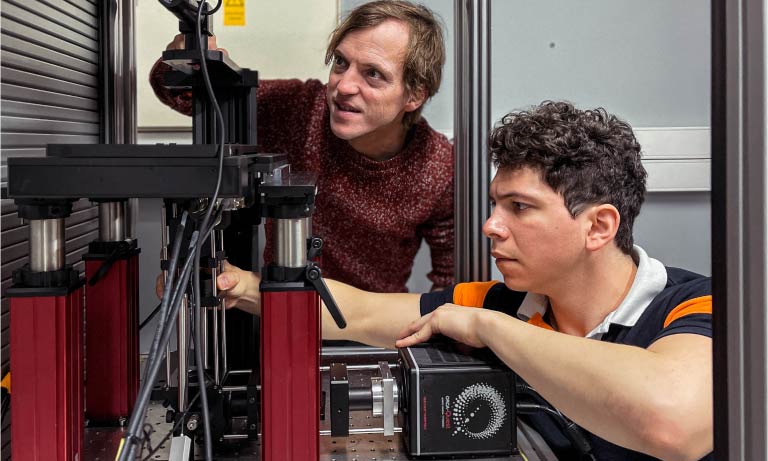
製作した "LowLiteScope "を使用するMichael Krieg 様と大学院生のLuis Felipe Morales-Curiel 様
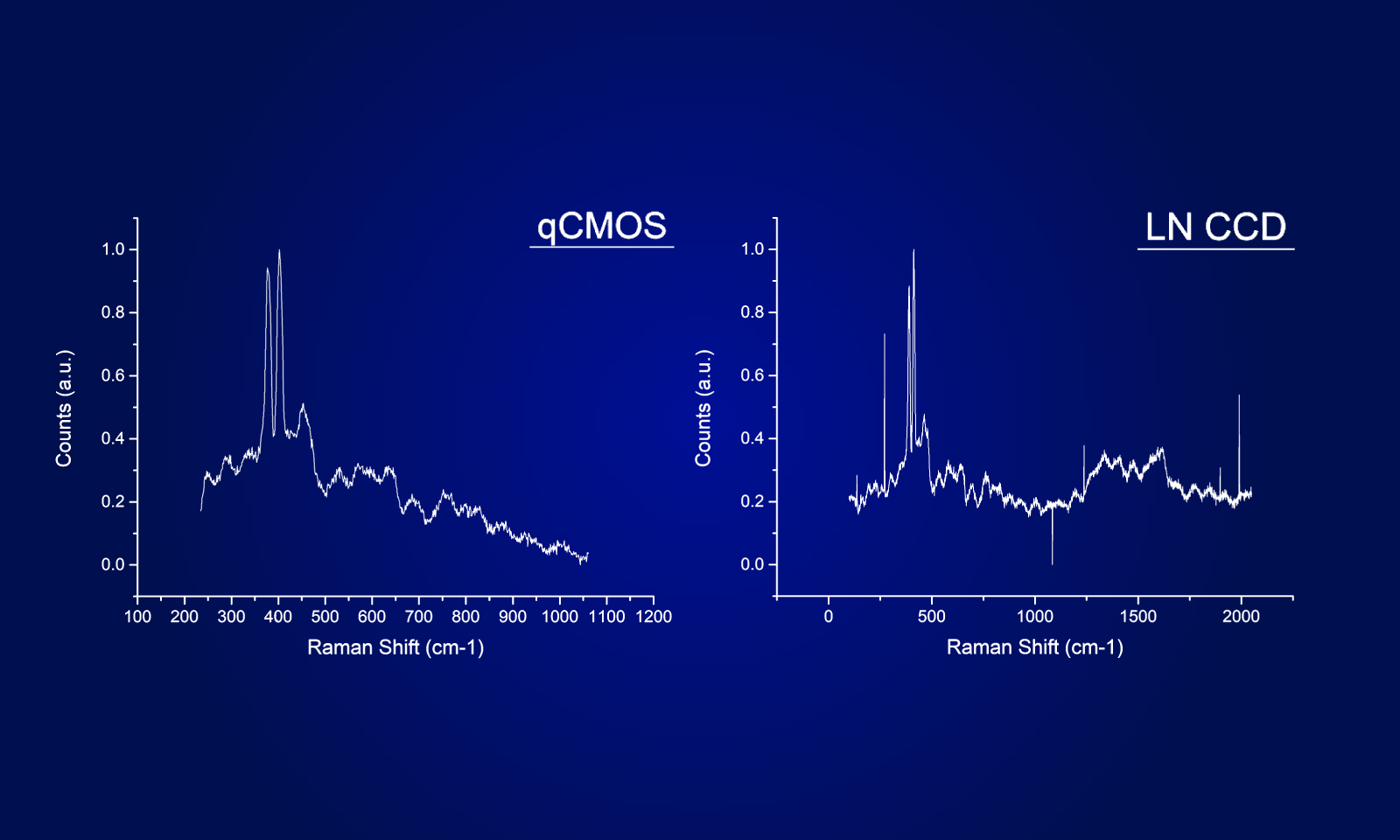
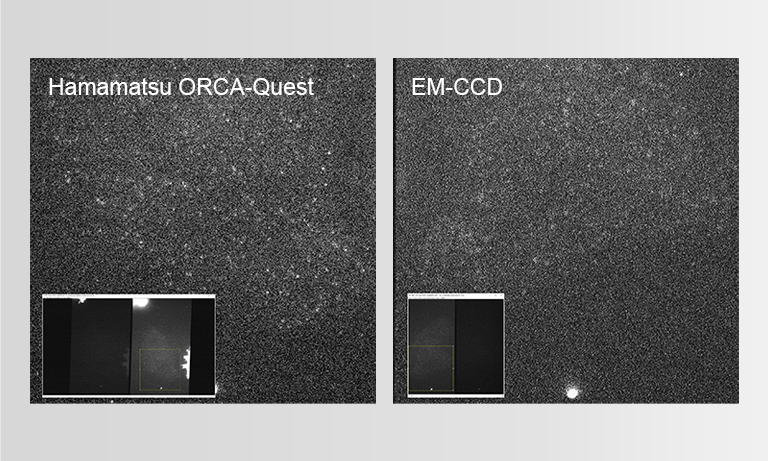
ORCAⓇ-Quest qCMOSⓇカメラによるイメージング
今回の実験では、ORCA-Quest qCMOSカメラを使用しました。0.27 e-という極めて低い読み出しノイズと高い量子効率により、ほぼ単一光子レベルまで識別可能なS/Nを実現したカメラです。
ORCA-Questの4.6 μm × 4.6 μmという画素サイズは、集光効率と空間分解能の面でLowLiteScopeの光学系に非常に適しており、これらを組み合わせることで、高画質な画像を取得することができました。
また、ORCA-Questの画素数は9.4万画素と多く、視野を犠牲にする必要はありません。さらに、この画素サイズと画素数は、「LowLiteScope」の3次元撮影のスピード向上にも貢献しています。ORCA-Questの小さな画素サイズと多画素数により、3次元ライトフィールドを2次元カメラセンサーに投影し、生物発光を用いた線虫全体の高速3次元撮影を可能にしました。従来のライトフィールドイメージングでは、3次元オブジェクトの複雑な計算による再構成が必要で、最大で30分もの時間がかかることもありました。このプロセスを高速化するために、ニューラルネットワークを採用し、3次元再構成にかかる時間を100ミリ秒に短縮しました。この方式を用いることで、5秒の露光時間で満足のいく結果を得られるようになりました。
また、露光時間をさらに短縮するために、再構成の前にCAREを適用しました。これにより、信号強度を維持しながら、露光時間をさらに20分の1まで短縮することができました。5ボリューム/秒での生物発光AI再構成ライトフィールド顕微鏡の例を、以下の応用例2に示します。
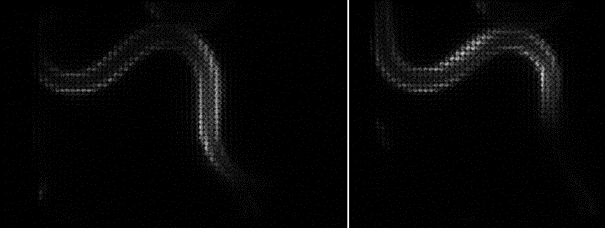
応用例2 : 自由行動下の線虫の筋肉にある生物発光カルシウムレポーターのライトフィールド画像
結果と今後の応用について
Luis Felipe Morales-CurielとMichael Krieg博士は、生物発光顕微鏡を生物学者にとっての汎用的なサンプル観察手法として確立しました。生物発光は、蛍光に比べて試料へのストレスが少なく、バックグラウンドノイズが少ないという利点があります。一方で、生物発光顕微鏡は得られる信号量が低く、それに伴って露光時間を長くする必要があるという欠点がありました。これに対し、最も明るい生物発光色素の使用や、低シグナルの感度に最適化された機器によるデータ記録、最新の機械学習ベースのアプローチによるデータ処理など、イメージングに関わる一連の機器構成全体を最適化することでこの欠点を克服しました。
Krieg博士の研究室では、この生物発光フレームワークを用いて、線虫や他のモデル生物、幹細胞由来のオルガノイドのメカノバイオロジーと神経科学の研究をさらに進める予定です。最近の研究において、このフレームワークは、光子ベースのシナプス伝達経路を確立するためのカルシウムトリガーフォトンエミッターの性能を可視化するために応用されました。
Michael Krieg博士について

Michael Krieg 博士は、スタンフォード大学の分子・細胞生理学教室 の元博士研究員。Miriam Goodman博士の研究室にて、モデル生物である線虫のニューロンにおける基本的な機械的シグナル伝達経路を研究。その後、ドレスデン工科大学にて発生生物学/生物物理学の博士号を取得。現在は、スペインのICFOのNeurophotonicsとMechanical Systems Biology Research Groupのグループリーダーを務めている。
※ 本ページに掲載している内容は取材時点のものです。
参考文献
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-022-04292-x
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41592-023-01836-9
- Read the full research paper here: https://rdcu.be/c9Re5
関連製品
ORCA-Quest 2は、ORCA-Questの後継機として極めて低ノイズなスキャンモードにおける読み出し速度の高速化や紫外領域での感度向上を実現。更なる進化を遂げた新たなqCMOSカメラです。
その他のお客様導入事例
- Confirmation
-
It looks like you're in the . If this is not your location, please select the correct region or country below.
You're headed to Hamamatsu Photonics website for JP (Japanese). If you want to view an other country's site, the optimized information will be provided by selecting options below.
In order to use this website comfortably, we use cookies. For cookie details please see our cookie policy.
- Cookie Policy
-
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in this cookie policy. By closing the cookie warning banner, scrolling the page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to the use of cookies.
Hamamatsu uses cookies in order to enhance your experience on our website and ensure that our website functions.
You can visit this page at any time to learn more about cookies, get the most up to date information on how we use cookies and manage your cookie settings. We will not use cookies for any purpose other than the ones stated, but please note that we reserve the right to update our cookies.
1. What are cookies?
For modern websites to work according to visitor’s expectations, they need to collect certain basic information about visitors. To do this, a site will create small text files which are placed on visitor’s devices (computer or mobile) - these files are known as cookies when you access a website. Cookies are used in order to make websites function and work efficiently. Cookies are uniquely assigned to each visitor and can only be read by a web server in the domain that issued the cookie to the visitor. Cookies cannot be used to run programs or deliver viruses to a visitor’s device.
Cookies do various jobs which make the visitor’s experience of the internet much smoother and more interactive. For instance, cookies are used to remember the visitor’s preferences on sites they visit often, to remember language preference and to help navigate between pages more efficiently. Much, though not all, of the data collected is anonymous, though some of it is designed to detect browsing patterns and approximate geographical location to improve the visitor experience.
Certain type of cookies may require the data subject’s consent before storing them on the computer.
2. What are the different types of cookies?
This website uses two types of cookies:
- First party cookies. For our website, the first party cookies are controlled and maintained by Hamamatsu. No other parties have access to these cookies.
- Third party cookies. These cookies are implemented by organizations outside Hamamatsu. We do not have access to the data in these cookies, but we use these cookies to improve the overall website experience.
3. How do we use cookies?
This website uses cookies for following purposes:
- Certain cookies are necessary for our website to function. These are strictly necessary cookies and are required to enable website access, support navigation or provide relevant content. These cookies direct you to the correct region or country, and support security and ecommerce. Strictly necessary cookies also enforce your privacy preferences. Without these strictly necessary cookies, much of our website will not function.
- Analytics cookies are used to track website usage. This data enables us to improve our website usability, performance and website administration. In our analytics cookies, we do not store any personal identifying information.
- Functionality cookies. These are used to recognize you when you return to our website. This enables us to personalize our content for you, greet you by name and remember your preferences (for example, your choice of language or region).
- These cookies record your visit to our website, the pages you have visited and the links you have followed. We will use this information to make our website and the advertising displayed on it more relevant to your interests. We may also share this information with third parties for this purpose.
Cookies help us help you. Through the use of cookies, we learn what is important to our visitors and we develop and enhance website content and functionality to support your experience. Much of our website can be accessed if cookies are disabled, however certain website functions may not work. And, we believe your current and future visits will be enhanced if cookies are enabled.
4. Which cookies do we use?
There are two ways to manage cookie preferences.
- You can set your cookie preferences on your device or in your browser.
- You can set your cookie preferences at the website level.
If you don’t want to receive cookies, you can modify your browser so that it notifies you when cookies are sent to it or you can refuse cookies altogether. You can also delete cookies that have already been set.
If you wish to restrict or block web browser cookies which are set on your device then you can do this through your browser settings; the Help function within your browser should tell you how. Alternatively, you may wish to visit www.aboutcookies.org, which contains comprehensive information on how to do this on a wide variety of desktop browsers.
5. What are Internet tags and how do we use them with cookies?
Occasionally, we may use internet tags (also known as action tags, single-pixel GIFs, clear GIFs, invisible GIFs and 1-by-1 GIFs) at this site and may deploy these tags/cookies through a third-party advertising partner or a web analytical service partner which may be located and store the respective information (including your IP-address) in a foreign country. These tags/cookies are placed on both online advertisements that bring users to this site and on different pages of this site. We use this technology to measure the visitors' responses to our sites and the effectiveness of our advertising campaigns (including how many times a page is opened and which information is consulted) as well as to evaluate your use of this website. The third-party partner or the web analytical service partner may be able to collect data about visitors to our and other sites because of these internet tags/cookies, may compose reports regarding the website’s activity for us and may provide further services which are related to the use of the website and the internet. They may provide such information to other parties if there is a legal requirement that they do so, or if they hire the other parties to process information on their behalf.
If you would like more information about web tags and cookies associated with on-line advertising or to opt-out of third-party collection of this information, please visit the Network Advertising Initiative website http://www.networkadvertising.org.
6. Analytics and Advertisement Cookies
We use third-party cookies (such as Google Analytics) to track visitors on our website, to get reports about how visitors use the website and to inform, optimize and serve ads based on someone's past visits to our website.
You may opt-out of Google Analytics cookies by the websites provided by Google:
https://tools.google.com/dlpage/gaoptout?hl=en
As provided in this Privacy Policy (Article 5), you can learn more about opt-out cookies by the website provided by Network Advertising Initiative:
http://www.networkadvertising.org
We inform you that in such case you will not be able to wholly use all functions of our website.
Close